How to Build Cummulitive Charts
The Competitive Edge for Modern Project Managers
How to Build a Cumulative Flow Diagram (Using the Template)
A Cumulative Flow Diagram (CFD) visualizes how work items move through your workflow over time. It helps you spot bottlenecks, manage Work in Progress (WIP), and understand throughput and lead time trends. This guide shows how to fill the Excel template and produce a clear CFD.
Donwload templates in Downlaods
What’s in the Template
- Day (or Date) – The daily time index for your sprint or flow-based period.
- Workflow columns – State counts for each day, typically:
- Backlog (not yet committed)
- To Do (committed, not started)
- In Progress
- Review / Test (optional, if you use it)
- Done (completed)
Important: Each workflow state should be a count of items at the end of that day. The chart will stack these counts to show cumulative totals.
Before You Start
- Define your workflow states (columns) in the exact order work flows from left to right.
- Decide the tracking period (e.g., 10–20 working days for a sprint, or a continuous monthly window for Kanban).
- Agree on a daily cutoff time (e.g., 5:00pm). You’ll record state counts as of that time each day.
Step 1 — Set the Timeline
- In the Day/Date column, list each day you’ll track.
- If you do not work weekends, either omit them or include them with repeated counts from the previous working day (so the chart stays continuous).
Step 2 — Record Daily State Counts
- At your cutoff time each day, count the number of items in each state:
- How many are in Backlog?
- How many are in To Do?
- How many are In Progress?
- How many are in Review/Test (if used)?
- How many are Done?
- Enter those counts into the row for that day. Do not enter daily deltas; enter the current counts per state.
Step 3 — Validate the Totals
Optionally, add a check column to ensure the sum of all states equals the current total scope for that day:
- If your state columns are in B:E (Backlog, To Do, In Progress, Done), use a check like
=SUM(B2:E2)for each row. - If scope grows or shrinks, the total will change. That’s okay—CFDs show this clearly.
Step 4 — Create the Cumulative Flow Chart (Stacked Area)
- Select the full table (Day/Date plus all state columns for all days).
- Insert a Stacked Area chart:
- X-axis: Day/Date
- Series: Each workflow state (Backlog, To Do, In Progress, Review/Test, Done)
- Order the series in the same left-to-right flow as your process. Typically, Backlog at the bottom and Done at the top (or vice versa) as long as you remain consistent.
- Name the chart (e.g., “Sprint 14 Cumulative Flow Diagram”).
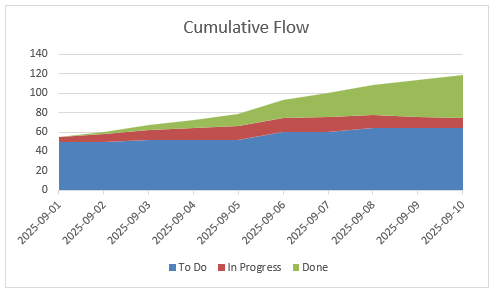
How to Read the CFD
- Band thickness = WIP in that state. A thicker band means more items are sitting in that column.
- Overall height = total scope. If the top of the chart rises, scope is increasing; if it falls, scope is decreasing.
- Done band slope = throughput. The steeper the top edge of the Done band, the faster you finish items per day.
- Horizontal distance of a band ≈ lead time in that state. If items spend many days in a column, that band stretches horizontally.
Daily Workflow and Updates
- At the end of each day, update the counts for each state.
- Refresh the chart (it will update automatically if it references the table range).
- Call out any sudden band changes (scope added/removed, blockage resolved, policy changed, etc.).
Common Real-World Situations
- Scope changes: If new items are added to Backlog or To Do, the total height increases. If items are removed, it decreases. This is normal and visible in the CFD.
- Blocked items: If In Progress (or Review/Test) band thickens over several days, you likely have a bottleneck. Investigate causes and reduce WIP.
- WIP limits: If you enforce limits per column, large band growth signals the limit was exceeded or items are not flowing smoothly.
- Partial days: If you miss a day, duplicate the last known counts to keep the chart continuous (note it in your log).
Optional Calculations (Helpful Metrics)
- Daily Throughput: Approximate as the daily increase in Done (e.g.,
Done_today - Done_yesterday). - Average WIP: Average of daily counts in In Progress (or sum across active states) over your period.
- Little’s Law (rough check): Average Lead Time ≈ Average WIP ÷ Average Throughput. Use as a trend indicator, not an absolute.
Quality Checks
- Monotonic Done: The Done count should never decrease over time.
- No negative counts: All state counts must be zero or positive integers.
- Consistent totals: The sum of all states each day should match your real total for that day.
- Correct series order: Ensure states are stacked in process order; it makes the CFD easier to interpret.
Interpretation Tips
- If In Progress grows while Done stays flat, items are starting but not finishing—reduce WIP, swarm, or remove blockers.
- If Review/Test balloons, you may have a testing or QA bottleneck—rebalance skills or adjust policies.
- If the top line rises rapidly, scope is expanding—reassess goals and capacity or renegotiate scope.
- A steady climb in Done with stable WIP bands usually indicates a healthy, predictable flow.
Keeping the CFD Useful
- Update it daily at the same time.
- Discuss it in standups or reviews to make flow issues visible early.
- Pair it with explicit WIP limits and clear “Definition of Done” to maintain quality and predictability.
Summary
Record daily counts per workflow state, insert a Stacked Area chart, and keep the series ordered by your process flow. Read band thickness for WIP, top-line height for scope, and the Done slope for throughput. Use what you see to manage bottlenecks, control WIP, and improve predictability.
| Date | To Do | In Progress | Done |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2025-09-01 | 50 | 5 | 0 |
| 2025-09-02 | 50 | 8 | 2 |
| 2025-09-03 | 52 | 10 | 5 |
| 2025-09-04 | 52 | 12 | 8 |
| 2025-09-05 | 52 | 14 | 13 |
| 2025-09-06 | 60 | 15 | 18 |
| 2025-09-07 | 60 | 16 | 24 |
| 2025-09-08 | 64 | 14 | 30 |
| 2025-09-09 | 64 | 12 | 38 |
| 2025-09-10 | 64 | 10 | 45 |
Leadership for Project Managers Course
Lead with clarity, confidence, and real impact. This Leadership for Project Managers course turns day-to-day challenges—unclear priorities, tough stakeholders, and cross-functional friction—into opportunities to guide teams and deliver outcomes that matter.
You’ll learn practical leadership skills tailored to project realities: setting direction without overcontrol, creating alignment across functions, and building commitment even when authority is limited. We go beyond theory with tools you can use immediately—one-sentence visioning, stakeholder influence maps, decision framing, and feedback scripts that actually land.
Expect hands-on frameworks, real-world examples, and guided practice to prepare for tough moments—executive readouts, resistance from stakeholders, and high-stakes negotiations. Downloadable templates and checklists keep everything actionable when the pace gets intense.
Ready to influence without waiting for a bigger title? Join a community of ambitious PMs, sharpen your edge, and deliver with purpose—project after project.
Take Control of Project Performance!
HK School of Management helps you go beyond status reports and gut feelings. In this advanced course, you’ll master Earned Value Management (EVM) to objectively measure progress, forecast outcomes, and take corrective action with confidence. Learn how WBS quality drives performance, how control accounts really work, and how to use EAC, TCPI, and variance analysis to make smarter decisions—before projects drift off track. Built around real-world examples and hands-on exercises, this course gives you practical tools you can apply immediately. Backed by our 30-day money-back guarantee—low risk, high impact for serious project professionals.
Learn More HKSM
HKSM
